We treat conditioned crawlspaces just like a very shallow basement. Please refer to 7.1 Basement, New Construction for a narrative of our approach.
Note: With appropriate detailing and maintenance, vented crawlspaces in new construction are also okay in many Pacific Northwest locations. For guidance, refer to 8.4 Retrofit Option 2: Vented with Floor Encapsulation.
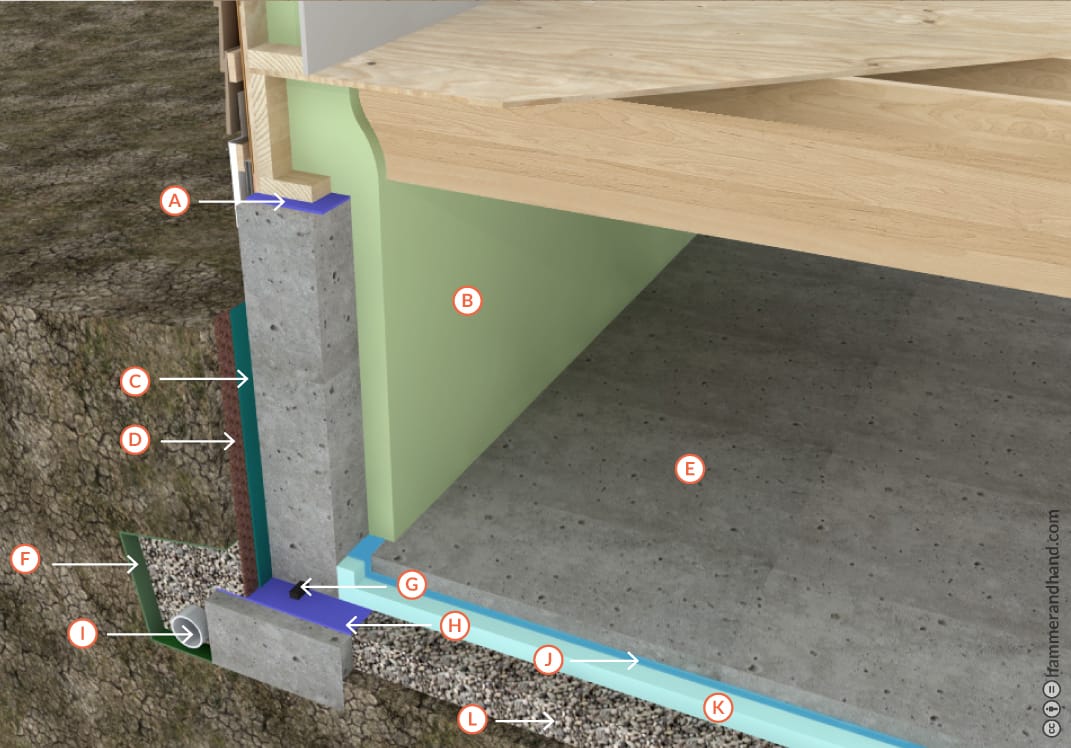
A. CAPILLARY BREAK
B. MEDIUM DENSITY SPRAY FOAM (MDSPF)
C. FLUID APPLIED ELASTOMERIC MEMBRANE
D. DIMPLED DRAINAGE MEMBRANE WITH GEOTEXTILE FABRIC
E. 2” CONCRETE SLAB, “RAT SLAB”
F. HEAVY DUTY GEOTEXTILE FILTER FABRIC
G. WATERSTOP
H. CAPILLARY BREAK
I. 4” DRAINAGE PIPE, HOLES DOWN
J. 12 MIL REINFORCED SOIL BARRIER WITH JOINTS LAPPED, TAPED, AND SEALED
B. MEDIUM DENSITY SPRAY FOAM (MDSPF)
C. FLUID APPLIED ELASTOMERIC MEMBRANE
D. DIMPLED DRAINAGE MEMBRANE WITH GEOTEXTILE FABRIC
E. 2” CONCRETE SLAB, “RAT SLAB”
F. HEAVY DUTY GEOTEXTILE FILTER FABRIC
G. WATERSTOP
H. CAPILLARY BREAK
I. 4” DRAINAGE PIPE, HOLES DOWN
J. 12 MIL REINFORCED SOIL BARRIER WITH JOINTS LAPPED, TAPED, AND SEALED
K. 2”-4” RIGID SUB-SLAB INSULATION (XPS OR EPS)
L. MINIMUM 4” LAYER WASHED AND CLEANED (NO FINES) CRUSHED STONE OR GRAVEL ALSO CONNECTED TO FOOTING DRAIN WITH PIPE/SLEEVES CAST INTO FOOTING
M. NOT SHOWN: IF RIGID FOAM INSULATION IS USED ON AN EXTERIOR WALL, PROTECT THE TOP WITH A COATING OR PROTECTION BOARD. BELOW GRADE, PLACE INSULATION BETWEEN DIMPLE DRAINAGE MAT AND ELASTOMERIC WATERPROOF MEMBRANE. FOAM MUST BE PROTECTED WITH DURABLE FINISH WHEN EXTENDED ABOVE GRADE.
L. MINIMUM 4” LAYER WASHED AND CLEANED (NO FINES) CRUSHED STONE OR GRAVEL ALSO CONNECTED TO FOOTING DRAIN WITH PIPE/SLEEVES CAST INTO FOOTING
M. NOT SHOWN: IF RIGID FOAM INSULATION IS USED ON AN EXTERIOR WALL, PROTECT THE TOP WITH A COATING OR PROTECTION BOARD. BELOW GRADE, PLACE INSULATION BETWEEN DIMPLE DRAINAGE MAT AND ELASTOMERIC WATERPROOF MEMBRANE. FOAM MUST BE PROTECTED WITH DURABLE FINISH WHEN EXTENDED ABOVE GRADE.
Ventilation: Code requires 1.0 CFM of continuous mechanical exhaust for each 50 square feet. For example, a 1000sf crawlspace will need 20cfm of ventilation. Ideally this is provided by a Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV).

