GLASSWOOD
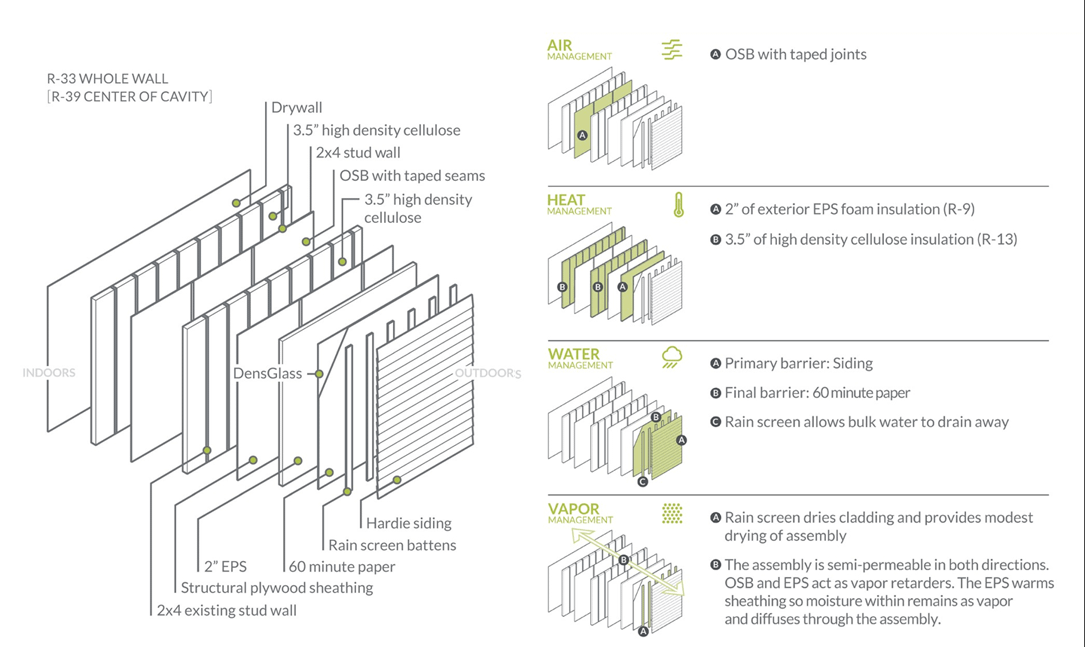
As a Passive House retrofit project (the first such effort on a commercial building in North America) Glasswood presented unique challenges to solve for in its high performance wall assembly design. Because code already required new exterior insulation, structural sheathing, and added fire resistance for the retrofit, the extra effort to attain Passive House certification – air sealing and thicker insulation – was modest. But the team did need to figure out what to do with the existing stud wall.
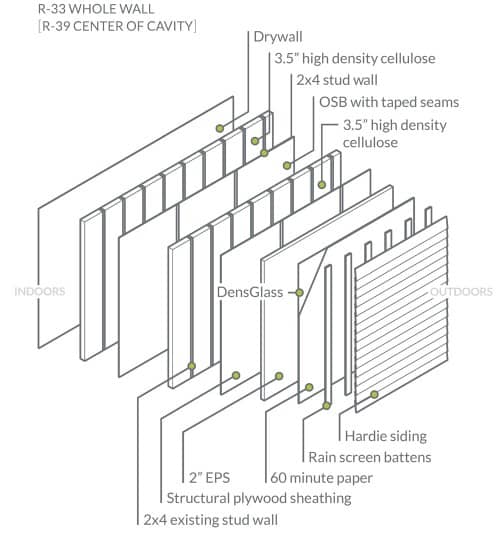
The air barrier for the project is a layer of OSB with taped seams, sandwiched between the existing 2×4 stud wall and a new 2×4 wall built immediately inboard. This location protects the air barrier from inadvertent occupant damage (nail holes from hanging artwork, for example).

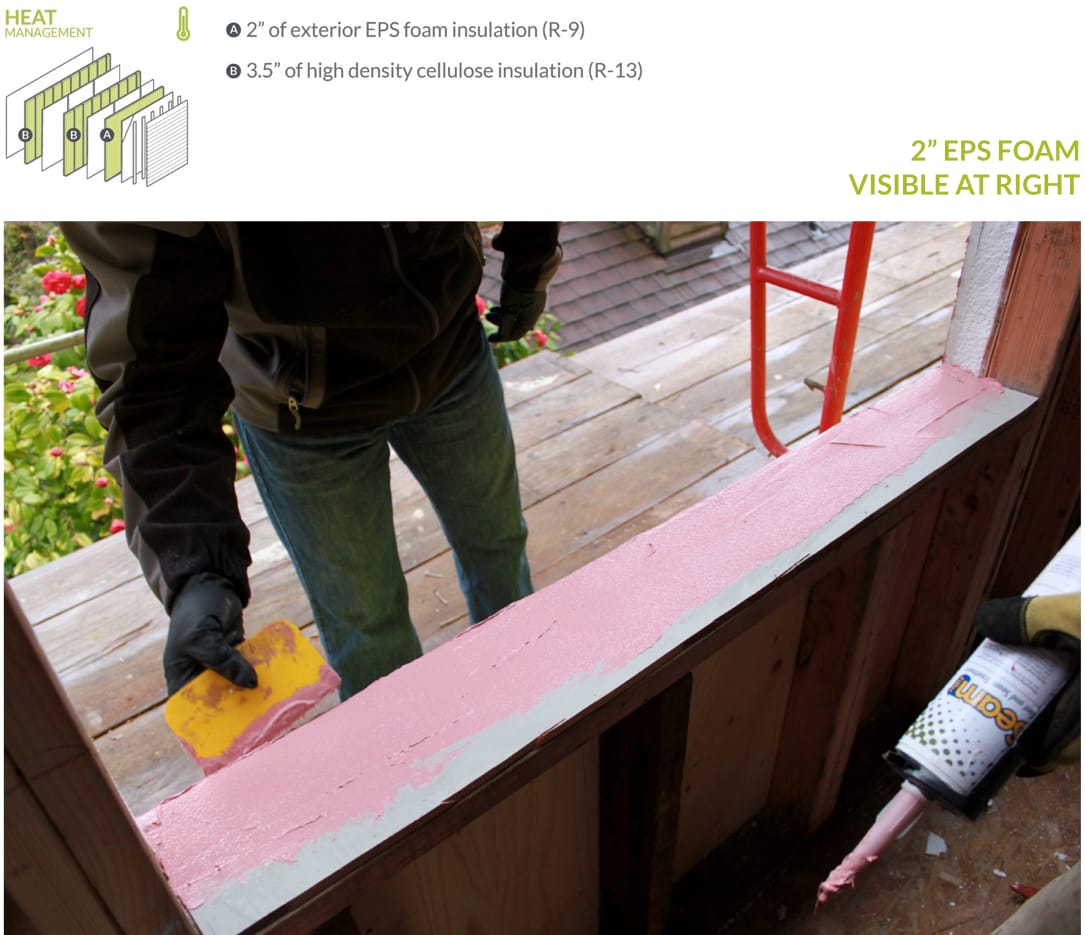
The two 2×4 stud walls are filled with high density cellulose insulation for a combined center of cavity insulative value of R-26. Two inches of continuous EPS foam insulation adds another R-9 to the assembly, and is only modestly thicker than the exterior insulation required by code. The sum of these three layers of insulation (plus sheet goods and air films) is R-33 whole wall and R-39 center of cavity.

Glasswood’s Hardie siding provides the first line of defense from water intrusion, with a rain screen cavity behind that allows water to drain away. 60 minute paper provides the water-resistive barrier, while a continuous layer of DensGlass immediately outboard of the EPS adds code-required fire resistance to the assembly.

Both the OSB and EPS are vapor retarders, making the assembly semi-vapor permeable in both directions. The EPS warms the structural plywood sheathing so that moisture remains in vapor form and can diffuse out of the assembly harmlessly. The ventilated rain screen cavity adds modest drying capacity to this semi-permeable assembly, but its main purpose in this context is to dry the cladding and facilitate drainage of bulk water.

A little extra insulation, a second stud wall, and a bit of attention to detail on air sealing brought a code-required envelope retrofit up to über-efficient Passive House energy performance. See an annotated photo tour of the assembly’s layers: